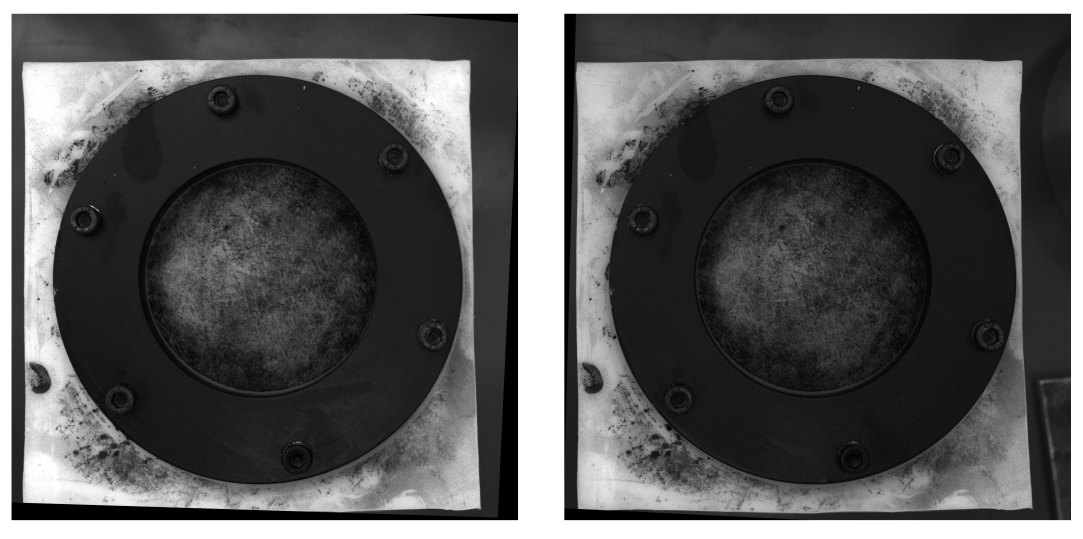
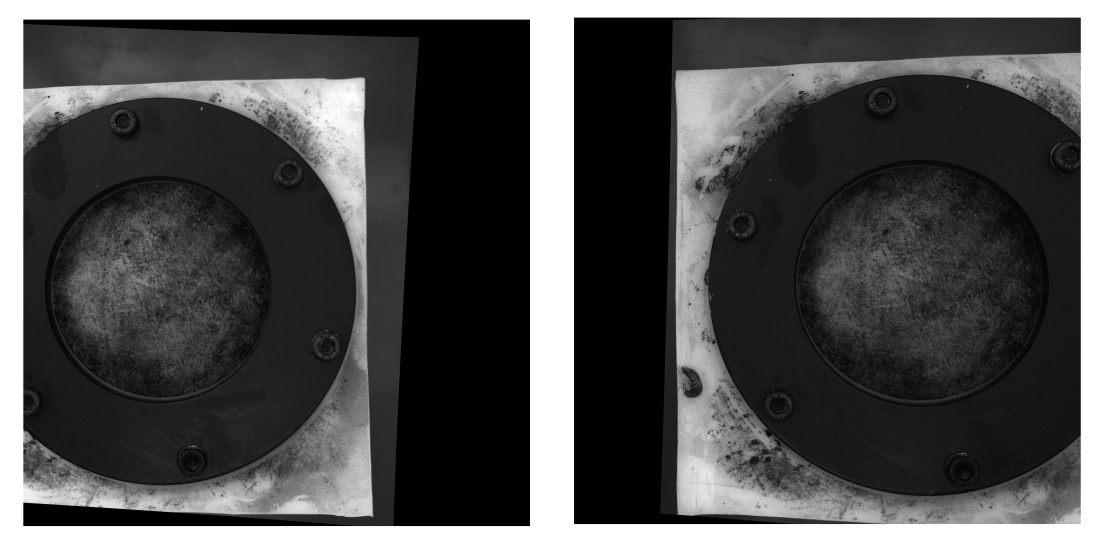
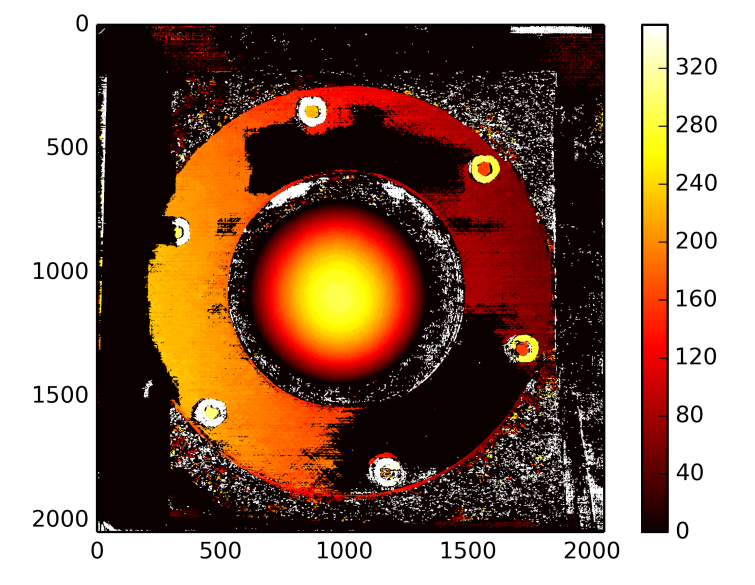
I m trying to get a depth map from an uncalibrated method. I can obtain the fundamental matrix via different correspondent points from SIFT method and "cv2.findFundamentalMat". Then with "cv2.stereoRectifyUncalibrated" i can get the rectification matrix. Finally i can use "cv2.warpPerspective" to rectify and compute the disparity but this latter doesnt conduct to a good depth map...The values are very high so i m wondering if i have to use "warpPerspective" or i have to calculate rotation matrix from homography matrix got with "stereoRectifyUncalibrated"
A part of the code :
#Obtainment of the correspondent point with SIFT
sift = cv2.SIFT()
###find the keypoints and descriptors with SIFT
kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(dst1,None)
kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(dst2,None)
###FLANN parameters
FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE = 0
index_params = dict(algorithm = FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE, trees = 5)
search_params = dict(checks=50)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params,search_params)
matches = flann.knnMatch(des1,des2,k=2)
good = []
pts1 = []
pts2 = []
###ratio test as per Lowe's paper
for i,(m,n) in enumerate(matches):
if m.distance < 0.8*n.distance:
good.append(m)
pts2.append(kp2[m.trainIdx].pt)
pts1.append(kp1[m.queryIdx].pt)
pts1 = np.array(pts1)
pts2 = np.array(pts2)
#Computation of the fundamental matrix
F,mask= cv2.findFundamentalMat(pts1,pts2,cv2.FM_LMEDS)
# Obtainment of the rectification matrix and use of the warpPerspective to transform them...
pts1 = pts1[:,:][mask.ravel()==1]
pts2 = pts2[:,:][mask.ravel()==1]
pts1 = np.int32(pts1)
pts2 = np.int32(pts2)
p1fNew = pts1.reshape((pts1.shape[0] * 2, 1))
p2fNew = pts2.reshape((pts2.shape[0] * 2, 1))
retBool ,rectmat1, rectmat2 = cv2.stereoRectifyUncalibrated(p1fNew,p2fNew,F,(2048,2048))
dst11 = cv2.warpPerspective(dst1,rectmat1,(2048,2048))
dst22 = cv2.warpPerspective(dst2,rectmat2,(2048,2048))