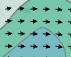
Hello. I created script to get arrows from the image. Im trying to detect orientation for each arrow. With my script i manage to get somewhat accurate results. The problem is that Im getting same results if arrows are oriented up or down, to the left or to the right. How to know if the arrow is pointing to left or to the right? In both cases of the pictures below i get same result around 90 deg.


original image
UPDATE 12.12.2016:
i manage to get it somewhat working by blurring the script picture more to get better contour. I then create bounding rectangle and split it in two parts and calculate surface area of each to get if arrows are facing up or down. Then I chose two points on bounding rectangle and calculate degrees from it. From degrees i then get wind direction.
Now bounding rectangle can sometimes be strangely oriented and giving slightly wrong directions. I think bounding ellipse is folowingmore appropriate but the results of degrees are not always correct since i cant set in which direction to check for the angle like i did in rectangle. How could i do the same with ellipse or just mathematically invert degree value based on arrow direction ?
#!/usr/bin/python
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import cv2
pyplot as plt
import math
img = cv2.imread('sample7.png')
import matplotlib.path as mplPath
from math import atan2, degrees, pi
def direction2(img):
height, width, channels = img.shape
img = cv2.resize(img, (width*8, height*8))
img = cv2.medianBlur(img,5)
cv2.medianBlur(img,9)
imgray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,th1 = cv2.threshold(imgray,100,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
cv2.threshold(imgray,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
edged=cv2.Canny(th1,127,200)
im2,contours,h = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(),cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
#return edged
(img2,cnts, _) = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
screenCnt=None
flag_t=False
flag_s=False
kot=[]
up_c=0
down_c=0
for c in cnts:
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP( c, 0.01*cv2.arcLength(c,True), True )
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
#print area
cv2.drawContours(img,[c],0,(0,255,0),1)
if int(len(approx)) > 8 and area > 600 500 and area < 1100:
anglelist=[]
1650:
#cv2.drawContours(img,[c],0,(0,255,0),1)
(x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(c)
center = (int(x),int(y))
ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(c)
(x,y),(MA,ma),angle = cv2.fitEllipse(c)
#cv2.ellipse(img,ellipse,(0,255,0),1)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
#print box
cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,0,255),1)
a= math.hypot(box[1][0] - box[0][0], box[1][1] - box[0][1])
b= math.hypot(box[3][0] - box[0][0], box[3][1] - box[0][1])
if a>b:
xos=(box[0][0]+box[1][0])/2
yos=(box[0][1]+box[1][1])/2
xos2=(box[2][0]+box[3][0])/2
yos2=(box[2][1]+box[3][1])/2
xosa=(box[1][0]+box[2][0])/2
yosa=(box[1][1]+box[2][1])/2
xos2a=(box[0][0]+box[3][0])/2
yos2a=(box[0][1]+box[3][1])/2
bbPath = mplPath.Path(np.array([[box[0][0], box[0][1]],[xos, yos],[xos2, yos2],[box[3][0], box[3][1]]]))
bbPath2 = mplPath.Path(np.array([[box[1][0], box[1][1]], [xos, yos], [xos2, yos2],[box[2][0], box[2][1]]]))
#pol=np.array([[box[1][0], box[1][1]], [xos, yos], [xos2, yos2],[box[2][0], box[2][1]]])
#cv2.drawContours(img,[pol],0,(0,0,255),1)
elif b>a:
xos=(box[1][0]+box[2][0])/2
yos=(box[1][1]+box[2][1])/2
xos2=(box[0][0]+box[3][0])/2
yos2=(box[0][1]+box[3][1])/2
xosa=(box[0][0]+box[1][0])/2
yosa=(box[0][1]+box[1][1])/2
xos2a=(box[2][0]+box[3][0])/2
yos2a=(box[2][1]+box[3][1])/2
bbPath = mplPath.Path(np.array([[box[0][0], box[0][1]],[box[1][0], box[1][1]], [xos, yos], [xos2, yos2]]))
bbPath2 = mplPath.Path(np.array([[box[3][0], box[3][1]],[box[2][0], box[2][1]], [xos, yos], [xos2, yos2]]))
#pol=np.array([[box[3][0], box[3][1]],[box[2][0], box[2][1]], [xos, yos], [xos2, yos2]])
#cv2.drawContours(img,[pol],0,(0,0,255),1)
r = 5 # accuracy
dots_down=[]
dots_up=[]
for dot in c:
result= bbPath.contains_point((dot[0][0], dot[0][1]),radius=r) or bbPath.contains_point((dot[0][0], dot[0][1]),radius=-r)
result2= bbPath2.contains_point((dot[0][0], dot[0][1]),radius=r) or bbPath2.contains_point((dot[0][0], dot[0][1]),radius=-r)
if result == True :
nov = [dot[0][0], dot[0][1]]
dots_down.append(nov)
if result2 == True :
nov = [dot[0][0], dot[0][1]]
dots_up.append(nov)
cv2.circle(img, (dot[0][0],dot[0][1]), 2, (255, 0, 0), -1)
#print nov
#if contour is closed
if cv2.isContourConvex(c):
down=np.array(dots_down)
up=np.array(dots_up)
area_down = cv2.contourArea(down)
area_up = cv2.contourArea(up)
else:
area_down = 20
area_up = 1
#print area_up
#print area_down
#print area_up
#print angle
if area_up > area_down:
up_c=up_c+1
#kot.append(round(angle,-1))
dx = xosa - xos2a
dy = yosa - yos2a
rads = atan2(-dy,dx)
rads %= 2*pi
degs = degrees(rads)
#print 'st:'
#print round(degs,-1)
#print round(angle,-1)
kot.append(round(degs,-1))
else:
down_c=down_c+1
#kot.append(round(angle,-1))
down_c=down_c+1
dx = xos2a - xosa
dy = yos2a - yosa
rads = atan2(-dy,dx)
rads %= 2*pi
degs = degrees(rads)
#print degs
kot.append(round(degs,-1))
cv2.drawContours(img, [approx], [c], -1, (0, 255, 255), 1)
(x,y),(MA,ma),angle = cv2.fitEllipse(c)
print round(angle,-1)
kot.append(round(angle,-1))
#cv2.circle(img, center, 1, (125, 125, 0), -1)
d = {}
if kot:
for elm in kot:
d[elm] = d.get(elm, 0) + 1
counts = [(j,i) for i,j in d.items()]
count, max_elm = max(counts)
print 'most common:'
print #print max_elm
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#preracunaj kot
if up_c > down_c and max_elm > 180:
max_elm=360-max_elm
elif up_c > down_c:
max_elm=max_elm
elif max_elm < 180:
max_elm=max_elm+180
else:
max_elm=max_elm
#print max_elm
if max_elm >= 337.5 and max_elm < 360:
smer = 'W'
elif max_elm >=0 and max_elm <22.5:
smer = 'W'
elif max_elm >=22.5 and max_elm <67.5:
smer = 'SE'
elif max_elm >=67.5 and max_elm <112.5:
smer = 'S'
elif max_elm >=112.5 and max_elm <157.5:
smer = 'SW'
elif max_elm >=157.5 and max_elm <202.5:
smer = 'E'
elif max_elm >=202.5 and max_elm <247.5:
smer = 'NE'
elif max_elm >=247.5 and max_elm <292.5:
smer = 'N'
elif max_elm >=292.5 and max_elm <337.5:
smer = 'NW'
else:
smer=0
return smer
#print smer
#cv2.imshow('img',img)
#cv2.waitKey(0)




