Measuring a Cube without depth
I'm trying to measure a cube without depth. I have the following information
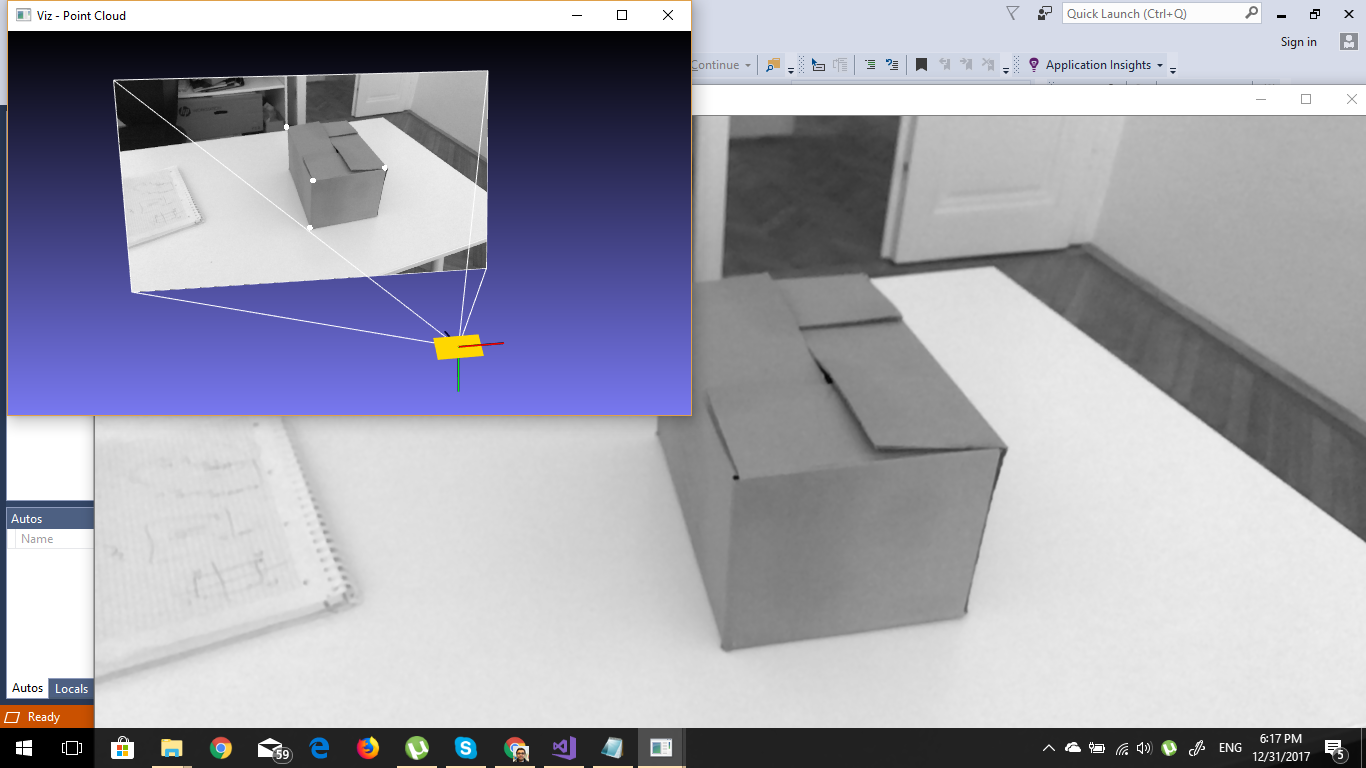
A plane that is position at 0,0,0 with normal up (0,1,0) Detected corners of the cube, I choose them using the click of the points. I convert the points into 3D using the inverse of camera matrix at Z = 1 Then I do line plane intersection to get 3D Positions of the clicked points. My problems 1. How do I correctly visualize the results, right now I'm trying to visualize a plane, but it's always centered at camera position 2. Is the process correct ? Is there are any other steps that I need to do ? 4. Giving camera position and orientation, How is that useful ?
Here is the picture progress so far
//Generate a camera intrinsic matrix
cv::Matx33d K;
K<< 1700, 0, src.cols / 2,
0, 1700, src.rows / 2,
0, 0, 1;
std::vector<cv::Vec3d> pointsTransformed3D;
Mat Pose = (Mat_<double>(3, 4)
<< 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0);
Mat H = (Mat_<double>(3,3));
Mat transposePose = (Mat_<double>(3, 3));
//transpose(Pose, transposePose);
//H = K*transposePose;
std::vector<cv::Vec3d> points3D;
for (int i = 0; i < corners.size(); i++)
{
cv::Vec3d pt;
pt[2] = 1.0f;
pt[0] = (corners[i].x);
pt[1] = (corners[i].y);
points3D.push_back(pt);
}
cv::transform(points3D, pointsTransformed3D, Pose);
std::vector<cv::Vec3d> points3DProjected;
cv::transform(pointsTransformed3D, points3DProjected, K.inv());
for (int i = 0; i < points3DProjected.size(); i++)
{
points3DProjected[i][0] = points3DProjected[i][0] / points3DProjected[i][2];
points3DProjected[i][1] = points3DProjected[i][1] / points3DProjected[i][2];
points3DProjected[i][2] = points3DProjected[i][2] / points3DProjected[i][2];
}
Mat rot = (Mat_<double>(3, 3)
<< 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1);
Mat translVec(3, 1, CV_64F);
translVec.at<double>(0, 0) = 0;
translVec.at<double>(1, 0) = 0;
translVec.at<double>(2, 0) = 0;
std::vector<Ray> rays;
for (int i = 0; i < points3DProjected.size(); i++)
{
Ray ray;
ray.origin = Vec3f(translVec.at<double>(0, 0), translVec.at<double>(1, 0),
translVec.at<double>(2, 0));
ray.direction = Vec3f(points3DProjected[i][0] - translVec.at<double>(0, 0),
points3DProjected[i][1] - translVec.at<double>(1, 0), points3DProjected[i][2] - translVec.at<double>(2, 0));
ray.direction = normalize(ray.direction);
rays.push_back(ray);
}
std::vector<cv::Vec3f> contacts;
for (int i = 0; i < points3DProjected.size(); i++)
{
Vec3f pt(0, 0, 0);
cv::Vec3f contact;
std::pair<bool, double> test = linePlaneIntersection(rays[i].direction, rays[i].origin, Vec3f(0, 1, 0), pt);
if (test.first == true)
{
cv::Vec3f contact(rays[i].origin + (rays[i].direction) * test.second);
contacts.push_back(contact);
}
}
//Project the 3D Point onto 2D plane
std::vector<cv::Point2d> points_2d;
std::vector<cv::Point3d> points_3d;
std::vector<cv::Point3d> lines_3d;
std::vector<cv::Point2d> lines_2d;
for (int i = 0; i < points3DProjected.size(); i++)
{
cv::Point3d pt;
pt.x = (points3DProjected[i][0]);
pt.y = (points3DProjected[i][1]);
pt.z = (points3DProjected[i][2]);
points_3d.push_back(pt);
}
// Create zero distortion
cv::Mat distCoeffs(4, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type);
distCoeffs.at<double>(0) = 0;
distCoeffs.at<double>(1) = 0;
distCoeffs ...