Issues with stereoRectify when camera orientations are very different
Remark: The coordinate system is right-handed, the cameras look into y-direction (rather then z).
I got a set of fixed, calibrated cameras which I want to use to get a disparity map of the scene. To do so I want to rectify the given images for a pair of cameras. However, the resulting rectified image is black and the roi`s returned by stereoRectify are either (0,0,0,0) or some very strange and small region of the image.
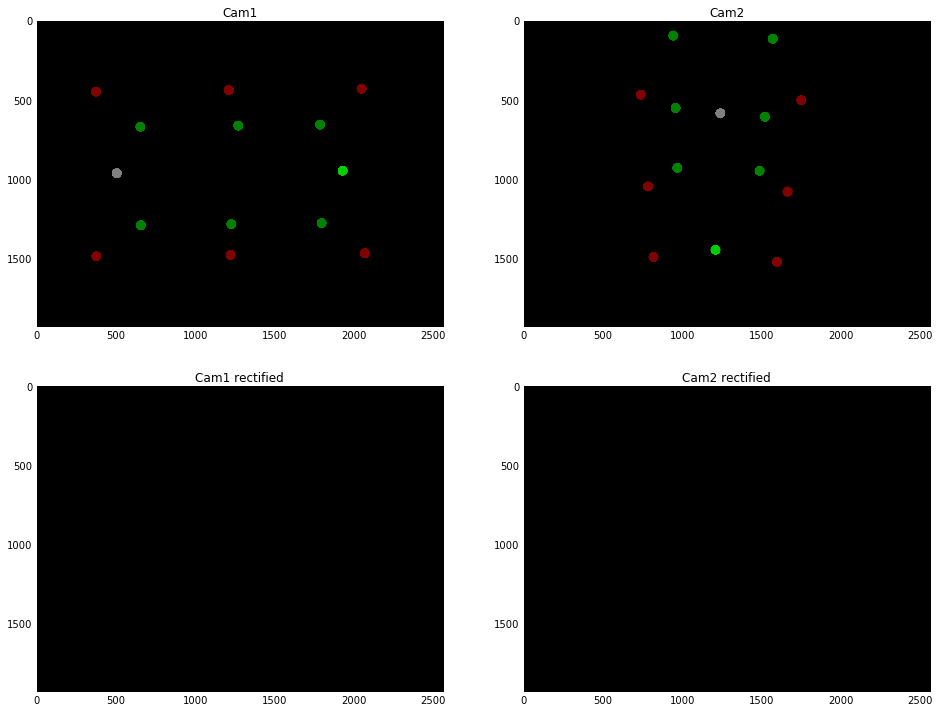
I suspect that my cameras are too far apart from each other and that their orientation differs too much. Is this indeed a problem or might there be some other issue?
My current workflow is as follows:
- Gather 2d-positions on the images of known 3d points
- stereoCalibrate the camera pair, retrieve their relative rotation (R) and translation (T)
- Use R and T for stereoRectify
- undistort the 'left and right image with initUndistortRectifyMap and remap
The full code to reproduce the result is posted below.
#%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
import numpy as np
# ============================
# Cameras
# ============================
Cam1 = {
'pos': np.array(
[72.5, 381.4, 43.3]),
'K': np.array([
[-3765.698429142333, 0.0000000000002, 1240.0306479725434],\
[0, -3765.6984291423264, 887.4632405702351],\
[0, 0, 1]]).astype('float'),
'R': np.array([
[0.9999370140766937, -0.011183065596097623, 0.0009523251859989448],\
[0.001403670192465846, 0.04042146114315272, -0.999181732813928],\
[0.011135420484979138, 0.9991201351804128, 0.04043461249593852]
]).T
}
Cam2 = {
'pos': np.array(
[315, 325, 50]),
'K': np.array([
[-3680, 0.000000000006, 1172],\
[0, -3680, 844],\
[0, 0, 1]]).astype('float'),
'R': np.array([
[-0.016444826412680857, 0.7399455721809343, -0.6724657001617901],\
[0.034691990397870555, -0.6717294370584418, -0.7399838033304401],\
[-0.9992627449707563, -0.03549807880687472, -0.014623710696333836]]
).T
}
W = 2560
H = 1920
Size = (W,H)
# ============================
# Data
# ============================
calib_A = np.array([20.0, 90.0, 50.0]) # Light-Green
calib_B = np.array([130.0, 90.0, 50.0]) # White
calib_C = np.array([ # Red
(10.0, 90.0, 10.0),
(75.0, 90.0, 10.0),
(140.0, 90.0, 10.0),
(140.0, 90.0, 90.0),
(75.0, 90.0, 90.0),
(10.0, 90.0, 90.0)
])
calib_D = np.array([ # Green
(20.0, 16.0, 20.0),
(75.0, 16.0, 20.0),
(130.0, 16.0, 20.0),
(130.0, 16.0, 80.0),
(70.0, 16.0, 80.0),
(20.0, 16.0, 80.0)
])
points3d = [calib_A, calib_B]
points3d.extend(calib_C)
points3d.extend(calib_D)
# ============================
# Various helper functions
# ============================
def img(Cam, points3d):
"""
Creates the 'photo' taken from a camera
"""
points2d = project_3d_to_2d(Cam, points3d)
I = np.zeros((H,W,3), "int8")
for i, p in enumerate(points2d):
color = (0, 50, 0)
if i == 1:
color = (255, 255, 255)
elif i > 1 and i < 8:
color = (255, 0, 0)
elif i >= 8:
color = (0, 255, 0)
center = (int(p[0]), int(p[1]))
cv2.circle(I, center, 32, color, -1)
return I
def project_3d_to_2d(Cam, points3d):
"""
This is a 'dummy' function to create the image for
the rectification/stereo-calibration.
"""
R = Cam['R']
pos = Cam['pos']
K = Cam['K'].astype('float32')
# pos to tvec
tvec = np.expand_dims ...