This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
Nice piece of code @Tetragramm !
I modified your code by "randomly" swapping the elements until it works as dealing with the 2 frame origins gave me some headaches and I didn't manage to make work your original code with the different line equations.
I also added by "brute force approach".
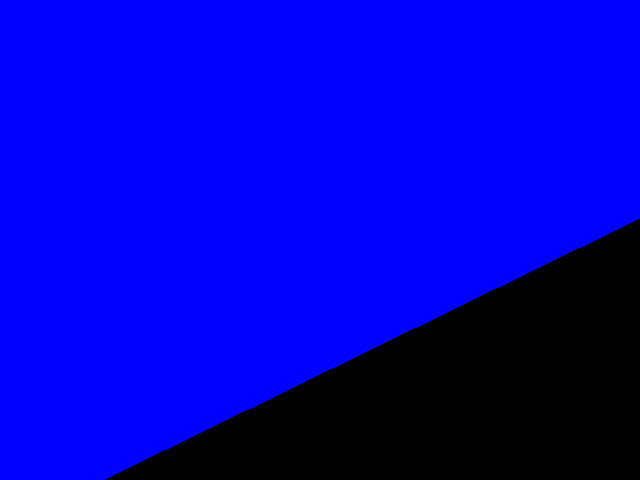
The result with pt1(20, 15), pt2(600, 385) in normal 2D frame:
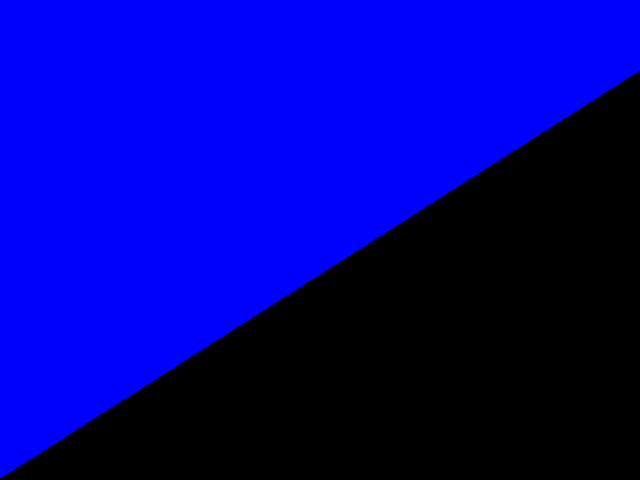
The result with pt1(50, 421), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:
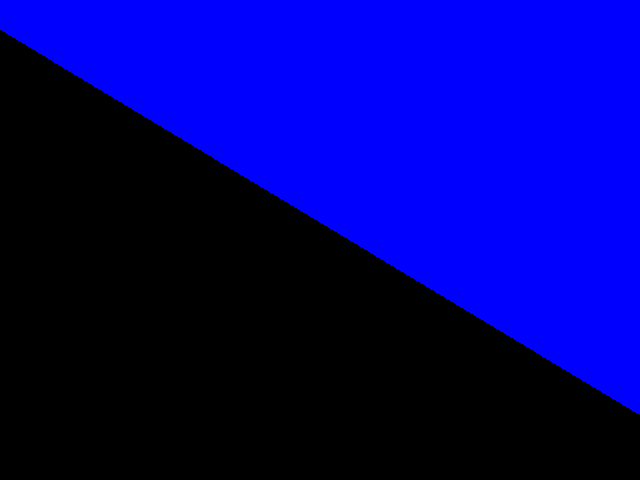
The result with pt1(0, 600), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:
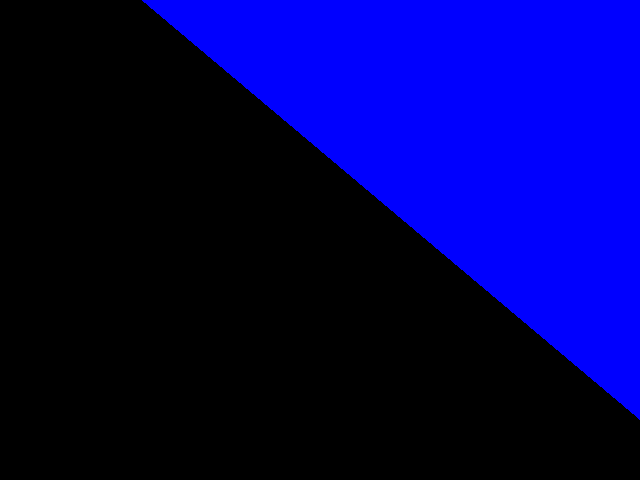
The result with pt1(0, -50), pt2(621, 253) in normal 2D frame:

The corresponding code:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
//@link: http://answers.opencv.org/question/87979/all-points-above-a-line/
//@author: Tetragramm
void drawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double m, const double b)
{
//Optimal way
int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols;
if(m > 0)
{
for(int y = 0; y < MAX(b,rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = MAX(0, (y-b)/m); x<cols; ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
else if(m == 0) {
//Trivial case
}
else
{
for(int y = 0; y < MIN(b, rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = 0; x < MIN(cols, (y-b)/m); ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
}
void calculateLineEquation(const cv::Point &pt1, const cv::Point &pt2, double &a, double &b)
{
a = (pt2.y - pt1.y) / (double) (pt2.x - pt1.x);
b = pt1.y - a*pt1.x;
}
void myDrawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double a, const double b)
{
//BruteForce
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
double x = j, y = img.rows - i;
if(a * x + b - y > 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
else if(a * x + b - y < 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(0,255,0);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
//Coordinates in regular 2D frame
//int x1 = 20, x2 = 600;
//int y1 = 15, y2 = 385;
//int x1 = 50, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 421, y2 = 77;
//int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 600, y2 = 77;
int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
int y1 = -50, y2 = 253;
cv::Mat img1 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3), img2 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3),
img3 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3);
cv::Point pt1(x1, img1.rows - y1), pt2(x2, img1.rows - y2);
cv::line(img3, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(0,0,255), 1);
double a = 0.0;
double b = 0.0;
calculateLineEquation(pt1, pt2, a, b);
std::cout << "Line equation in image space, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
drawPoints(img1, a, b);
calculateLineEquation(cv::Point(x1,y1), cv::Point(x2,y2), a, b);
std::cout << "Regular 2D frame, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
myDrawPoints(img2, a, b);
cv::imshow("img1", img1);
cv::imwrite("points_above_line.png", img1);
cv::imshow("img2", img2);
cv::imshow("img3", img3);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
Nice piece of code @Tetragramm !
I modified your code by "randomly" swapping the elements until it works as dealing with the 2 frame origins gave me some headaches and I didn't manage to make work your original code with the different line equations.
I also added by my "brute force approach".
The result with pt1(20, 15), pt2(600, 385) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(50, 421), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(0, 600), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(0, -50), pt2(621, 253) in normal 2D frame:

The corresponding code:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
//@link: http://answers.opencv.org/question/87979/all-points-above-a-line/
//@author: Tetragramm
void drawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double m, const double b)
{
//Optimal way
int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols;
if(m > 0)
{
for(int y = 0; y < MAX(b,rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = MAX(0, (y-b)/m); x<cols; ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
else if(m == 0) {
//Trivial case
}
else
{
for(int y = 0; y < MIN(b, rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = 0; x < MIN(cols, (y-b)/m); ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
}
void calculateLineEquation(const cv::Point &pt1, const cv::Point &pt2, double &a, double &b)
{
a = (pt2.y - pt1.y) / (double) (pt2.x - pt1.x);
b = pt1.y - a*pt1.x;
}
void myDrawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double a, const double b)
{
//BruteForce
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
double x = j, y = img.rows - i;
if(a * x + b - y > 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
else if(a * x + b - y < 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(0,255,0);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
//Coordinates in regular 2D frame
//int x1 = 20, x2 = 600;
//int y1 = 15, y2 = 385;
//int x1 = 50, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 421, y2 = 77;
//int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 600, y2 = 77;
int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
int y1 = -50, y2 = 253;
cv::Mat img1 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3), img2 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3),
img3 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3);
cv::Point pt1(x1, img1.rows - y1), pt2(x2, img1.rows - y2);
cv::line(img3, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(0,0,255), 1);
double a = 0.0;
double b = 0.0;
calculateLineEquation(pt1, pt2, a, b);
std::cout << "Line equation in image space, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
drawPoints(img1, a, b);
calculateLineEquation(cv::Point(x1,y1), cv::Point(x2,y2), a, b);
std::cout << "Regular 2D frame, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
myDrawPoints(img2, a, b);
cv::imshow("img1", img1);
cv::imwrite("points_above_line.png", img1);
cv::imshow("img2", img2);
cv::imshow("img3", img3);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
 | 3 | No.3 Revision |
Nice piece of code @Tetragramm !
I modified your code by "randomly" swapping the elements until it works as dealing with the 2 frame origins gave me some headaches and I didn't manage to make work your original code with the different line equations.
I also added my "brute force approach".
The result with your (modified) approach:
The result with pt1(20, 15), pt2(600, 385) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(50, 421), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(0, 600), pt2(621, 77) in normal 2D frame:

The result with pt1(0, -50), pt2(621, 253) in normal 2D frame:

The corresponding code:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
//@link: http://answers.opencv.org/question/87979/all-points-above-a-line/
//@author: Tetragramm
void drawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double m, const double b)
{
//Optimal way
int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols;
if(m > 0)
{
for(int y = 0; y < MAX(b,rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = MAX(0, (y-b)/m); x<cols; ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
else if(m == 0) {
//Trivial case
}
else
{
for(int y = 0; y < MIN(b, rows); ++y)
{
for(int x = 0; x < MIN(cols, (y-b)/m); ++x)
{
//Do Stuff Here
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
}
}
}
void calculateLineEquation(const cv::Point &pt1, const cv::Point &pt2, double &a, double &b)
{
a = (pt2.y - pt1.y) / (double) (pt2.x - pt1.x);
b = pt1.y - a*pt1.x;
}
void myDrawPoints(cv::Mat &img, const double a, const double b)
{
//BruteForce
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
double x = j, y = img.rows - i;
if(a * x + b - y > 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(255,0,0);
}
else if(a * x + b - y < 0)
{
img.at<cv::Vec3b>(i, j) = cv::Vec3b(0,255,0);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
//Coordinates in regular 2D frame
//int x1 = 20, x2 = 600;
//int y1 = 15, y2 = 385;
//int x1 = 50, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 421, y2 = 77;
//int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
//int y1 = 600, y2 = 77;
int x1 = 0, x2 = 621;
int y1 = -50, y2 = 253;
cv::Mat img1 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3), img2 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3),
img3 = cv::Mat::zeros(480, 640, CV_8UC3);
cv::Point pt1(x1, img1.rows - y1), pt2(x2, img1.rows - y2);
cv::line(img3, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(0,0,255), 1);
double a = 0.0;
double b = 0.0;
calculateLineEquation(pt1, pt2, a, b);
std::cout << "Line equation in image space, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
drawPoints(img1, a, b);
calculateLineEquation(cv::Point(x1,y1), cv::Point(x2,y2), a, b);
std::cout << "Regular 2D frame, slope a=" << a << " ; ordinate at origin b=" << b << std::endl;
myDrawPoints(img2, a, b);
cv::imshow("img1", img1);
cv::imwrite("points_above_line.png", img1);
cv::imshow("img2", img2);
cv::imshow("img3", img3);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}