This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size. If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN to detect background than remove it from the original image. This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
Follow a simple function to do this. Getting on load honeycomb from @Petyu's question here
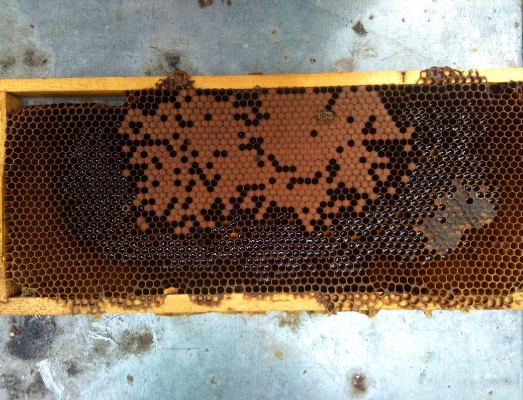

this is the result (minThickess=4):
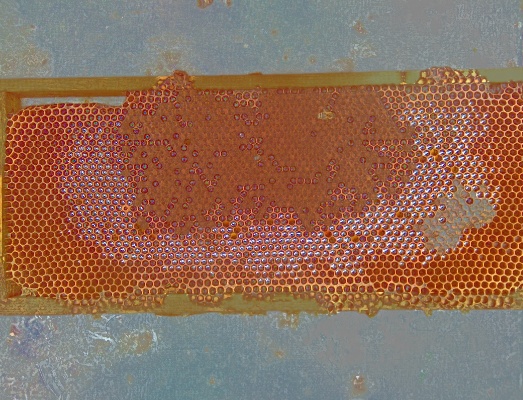

this is the background:
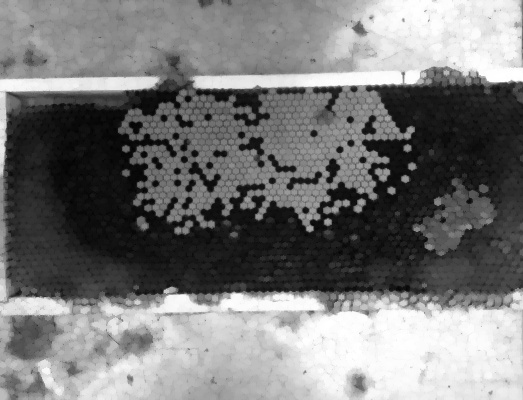
and this the code
/** @brief Remove non-uniform illumination using morphology
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size.
If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN
to detect background than remove it from the original image.
This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
@param [in]src input image GRAY, BGR or BGRA.
With BGR(A) image this function uses Brightness from image HSV.
@param [out]dst destination image. If alpha channel is present in src it will be cloned in dst
@param minThickess size used by morphology operation to estimate background. Use small size to
enhance details flatting larger structures.
@c minThickess should be just larger than maximum thickness in objects you want to keep.
Example:
- Take thickest object, suppose is circle 100 * 100px
- Measure its maximum thickness let's say is 20px: In this case @c minThickess could be 20+5.
- If the circle is filled than thickness=diameter, consequently @c minThickess should be 100+5px
@param restoreMean if true, the mean of input brightness will be restored in destination image.
if false, the destination brightness will be close to darker region of input image.
@param [out]background if not NULL the removed background will be returned here.
This will be Mat(src.size(),CV_8UC1)
*/
void NonUniformIlluminationMorph(const cv::Mat &src, cv::Mat &dst, int minThickess = 5, bool restoreMean = true, cv::Mat *background=NULL)
{
CV_Assert(minThickess >= 0);
CV_Assert((src.type() == CV_8UC1) || (src.type() == CV_8UC3) || (src.type() == CV_8UC4));
cv::Mat brightness, src_hsv;
vector<cv::Mat> hsv_planes;
// GET THE BRIGHTNESS
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
src.copyTo(brightness);
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(src_hsv, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
//to restore previous brightness we need its current mean
Scalar m;
if (restoreMean)
m = mean(brightness);
// REMOVE THE BACKGROUND
int size = minThickess / 2;
Point anchor = Point(size, size);
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_ELLIPSE, Size(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1), anchor);
if (background != NULL) // to keep background we need to use MORPH_OPEN
{
//get the background
cv::Mat bkg(brightness.size(), CV_8UC1);
morphologyEx(brightness, bkg, MORPH_OPEN, element, anchor);
//save the background
(*background) = bkg;
//remove the background
brightness = brightness - bkg;
}
else //tophat(I) <=> open(I) - I;
{
//remove background
morphologyEx(brightness, brightness, MORPH_TOPHAT, element, anchor);
}
// RESTORE PREVIOUS BRIGHTNESS MEAN
if (restoreMean)
brightness += m(0);
// BUILD THE DESTINATION
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
dst = brightness;
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
merge(hsv_planes, dst);
cvtColor(dst, dst, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
}
// restore alpha channel from source
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::Mat bgr;
vector<cv::Mat> bgr_planes = { hsv_planes[0], hsv_planes[1], hsv_planes[2]};
merge(bgr_planes, bgr);
cvtColor(bgr, bgr, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
int from_toA[] = { 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
src.copyTo(dst);
cv::mixChannels(&bgr, 1, &dst, 1, from_toA, 3);
}
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:SRC", src);
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:DST", dst);
if ((background != NULL) && (!background->empty()))
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:BKG", *background);
}
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size. If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN to detect background than remove it from the original image. This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
Follow Below is a simple function to do this. Getting on load honeycomb from @Petyu's question hereThis is a simple test (source and result)

this is the result (minThickess=4):

this is the background:



and this the code
/** @brief Remove non-uniform illumination using morphology
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size.
If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN
to detect background than remove it from the original image.
This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
@param [in]src input image GRAY, BGR or BGRA.
With BGR(A) image this function uses Brightness from image HSV.
@param [out]dst destination image. If alpha channel is present in src it will be cloned in dst
@param minThickess size used by morphology operation to estimate background. Use small size to
enhance details flatting larger structures.
@c minThickess should be just larger than maximum thickness in objects you want to keep.
Example:
- Take thickest object, suppose is circle 100 * 100px
- Measure its maximum thickness let's say is 20px: In this case @c minThickess could be 20+5.
- If the circle is filled than thickness=diameter, consequently @c minThickess should be 100+5px
@param restoreMean if true, the mean of input brightness will be restored in destination image.
if false, the destination brightness will be close to darker region of input image.
@param [out]background if not NULL the removed background will be returned here.
This will be Mat(src.size(),CV_8UC1)
*/
void NonUniformIlluminationMorph(const cv::Mat &src, cv::Mat &dst, int minThickess = 5, bool restoreMean = true, cv::Mat *background=NULL)
{
CV_Assert(minThickess >= 0);
CV_Assert((src.type() == CV_8UC1) || (src.type() == CV_8UC3) || (src.type() == CV_8UC4));
cv::Mat brightness, src_hsv;
vector<cv::Mat> hsv_planes;
// GET THE BRIGHTNESS
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
src.copyTo(brightness);
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(src_hsv, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
//to restore previous brightness we need its current mean
Scalar m;
if (restoreMean)
m = mean(brightness);
// REMOVE THE BACKGROUND
int size = minThickess / 2;
Point anchor = Point(size, size);
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_ELLIPSE, Size(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1), anchor);
if (background != NULL) // to keep background we need to use MORPH_OPEN
{
//get the background
cv::Mat bkg(brightness.size(), CV_8UC1);
morphologyEx(brightness, bkg, MORPH_OPEN, element, anchor);
//save the background
(*background) = bkg;
//remove the background
brightness = brightness - bkg;
}
else //tophat(I) <=> open(I) - I;
{
//remove background
morphologyEx(brightness, brightness, MORPH_TOPHAT, element, anchor);
}
// RESTORE PREVIOUS BRIGHTNESS MEAN
if (restoreMean)
brightness += m(0);
// BUILD THE DESTINATION
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
dst = brightness;
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
merge(hsv_planes, dst);
cvtColor(dst, dst, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
}
// restore alpha channel from source
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::Mat bgr;
vector<cv::Mat> bgr_planes = { hsv_planes[0], hsv_planes[1], hsv_planes[2]};
merge(bgr_planes, bgr);
cvtColor(bgr, bgr, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
int from_toA[] = { 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
src.copyTo(dst);
cv::mixChannels(&bgr, 1, &dst, 1, from_toA, 3);
}
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:SRC", src);
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:DST", dst);
if ((background != NULL) && (!background->empty()))
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:BKG", *background);
}
 | 3 | No.3 Revision |
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size. If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN to detect background than remove it from the original image. This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
MORPH_TOPHAT. Below is a simple function to do this. this.
This is the result on a simple test image (source and result)


and Test on complex image is here while this the codeis the code:
/** @brief Remove non-uniform illumination using morphology
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size.
If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN
to detect background than remove it from the original image.
This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
@param [in]src input image GRAY, BGR or BGRA.
With BGR(A) image this function uses Brightness from image HSV.
@param [out]dst destination image. If alpha channel is present in src it will be cloned in dst
@param minThickess size used by morphology operation to estimate background. Use small size to
enhance details flatting larger structures.
@c minThickess should be just larger than maximum thickness in objects you want to keep.
Example:
- Take thickest object, suppose is circle 100 * 100px
- Measure its maximum thickness let's say is 20px: In this case @c minThickess could be 20+5.
- If the circle is filled than thickness=diameter, consequently @c minThickess should be 100+5px
@param restoreMean if true, the mean of input brightness will be restored in destination image.
if false, the destination brightness will be close to darker region of input image.
@param [out]background if not NULL the removed background will be returned here.
This will be Mat(src.size(),CV_8UC1)
*/
void NonUniformIlluminationMorph(const cv::Mat &src, cv::Mat &dst, int minThickess = 5, bool restoreMean = true, cv::Mat *background=NULL)
{
CV_Assert(minThickess >= 0);
CV_Assert((src.type() == CV_8UC1) || (src.type() == CV_8UC3) || (src.type() == CV_8UC4));
cv::Mat brightness, src_hsv;
vector<cv::Mat> hsv_planes;
// GET THE BRIGHTNESS
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
src.copyTo(brightness);
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(src_hsv, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
//to restore previous brightness we need its current mean
Scalar m;
if (restoreMean)
m = mean(brightness);
// REMOVE THE BACKGROUND
int size = minThickess / 2;
Point anchor = Point(size, size);
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_ELLIPSE, Size(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1), anchor);
if (background != NULL) // to keep background we need to use MORPH_OPEN
{
//get the background
cv::Mat bkg(brightness.size(), CV_8UC1);
morphologyEx(brightness, bkg, MORPH_OPEN, element, anchor);
//save the background
(*background) = bkg;
//remove the background
brightness = brightness - bkg;
}
else //tophat(I) <=> open(I) - I;
{
//remove background
morphologyEx(brightness, brightness, MORPH_TOPHAT, element, anchor);
}
// RESTORE PREVIOUS BRIGHTNESS MEAN
if (restoreMean)
brightness += m(0);
// BUILD THE DESTINATION
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
dst = brightness;
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
merge(hsv_planes, dst);
cvtColor(dst, dst, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
}
// restore alpha channel from source
else if (dst.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::Mat bgr;
vector<cv::Mat> bgr_planes = { hsv_planes[0], hsv_planes[1], hsv_planes[2]};
merge(bgr_planes, bgr);
cvtColor(bgr, bgr, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
int from_toA[] = { 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
src.copyTo(dst);
cv::mixChannels(&bgr, 1, &dst, 1, from_toA, 3);
}
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:SRC", src);
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:DST", dst);
if ((background != NULL) && (!background->empty()))
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:BKG", *background);
}
 | 4 | No.4 Revision |
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size. If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN to detect background than remove it from the original image. This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT. Below is a simple function to do this.
This is the result on a simple image (source thanks to and result)


Test on complex image is here while this is the code:
[EDIT] corrected a small error
/** @brief Remove non-uniform illumination using morphology
Morphology OPEN can detects bright structures larger that a given size.
If you consider large structures as background you can use OPEN
to detect background than remove it from the original image.
This is same as to do MORPH_TOPHAT.
@param [in]src input image GRAY, BGR or BGRA.
With BGR(A) image this function uses Brightness from image HSV.
@param [out]dst destination image. If alpha channel is present in src it will be cloned in dst
@param minThickess size used by morphology operation to estimate background. Use small size to
enhance details flatting larger structures.
@c minThickess should be just larger than maximum thickness in objects you want to keep.
Example:
- Take thickest object, suppose is circle 100 * 100px
- Measure its maximum thickness let's say is 20px: In this case @c minThickess could be 20+5.
- If the circle is filled than thickness=diameter, consequently @c minThickess should be 100+5px
@param restoreMean if true, the mean of input brightness will be restored in destination image.
if false, the destination brightness will be close to darker region of input image.
@param [out]background if not NULL the removed background will be returned here.
This will be Mat(src.size(),CV_8UC1)
*/
void NonUniformIlluminationMorph(const cv::Mat &src, cv::Mat &dst, int minThickess = 5, bool restoreMean = true, cv::Mat *background=NULL)
{
CV_Assert(minThickess >= 0);
CV_Assert((src.type() == CV_8UC1) || (src.type() == CV_8UC3) || (src.type() == CV_8UC4));
cv::Mat brightness, src_hsv;
vector<cv::Mat> hsv_planes;
// GET THE BRIGHTNESS
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
src.copyTo(brightness);
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
else if (src.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::cvtColor(src, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
cv::cvtColor(src_hsv, src_hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV);
cv::split(src_hsv, hsv_planes);
brightness = hsv_planes[2];
}
//to restore previous brightness we need its current mean
Scalar m;
if (restoreMean)
m = mean(brightness);
// REMOVE THE BACKGROUND
int size = minThickess / 2;
Point anchor = Point(size, size);
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_ELLIPSE, Size(2 * size + 1, 2 * size + 1), anchor);
if (background != NULL) // to keep background we need to use MORPH_OPEN
{
//get the background
cv::Mat bkg(brightness.size(), CV_8UC1);
morphologyEx(brightness, bkg, MORPH_OPEN, element, anchor);
//save the background
(*background) = bkg;
//remove the background
brightness = brightness - bkg;
}
else //tophat(I) <=> open(I) - I;
{
//remove background
morphologyEx(brightness, brightness, MORPH_TOPHAT, element, anchor);
}
// RESTORE PREVIOUS BRIGHTNESS MEAN
if (restoreMean)
brightness += m(0);
// BUILD THE DESTINATION
if (src.type() == CV_8UC1)
dst = brightness;
else if (dst.type() (src.type() == CV_8UC3)
{
merge(hsv_planes, dst);
cvtColor(dst, dst, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
}
// restore alpha channel from source
else if (dst.type() (src.type() == CV_8UC4)
{
cv::Mat bgr;
vector<cv::Mat> bgr_planes = { hsv_planes[0], hsv_planes[1], hsv_planes[2]};
merge(bgr_planes, bgr);
cvtColor(bgr, bgr, COLOR_HSV2BGR);
int from_toA[] = { 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
src.copyTo(dst);
cv::mixChannels(&bgr, 1, &dst, 1, from_toA, 3);
}
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:SRC", src);
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:DST", dst);
if ((background != NULL) && (!background->empty()))
imshow("NonUniformIlluminationMorph:BKG", *background);
}