This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
you just need to know which rows you want to remove and then you can just use the removeRow() function below:
void removeRow(InputOutputArray _matIn, int row, int method = METHOD::CV_RECT)
{
CV_Assert( row >= 0 && row < _matIn.getMat().rows );
Mat matIn = _matIn.getMat();
cv::Size size = matIn.size();
Mat matOut( matIn.rows - 1, matIn.cols, matIn.type());
if ( row > 0 )
{
cv::Rect rect( 0, 0, size.width, row );
matIn( rect ).copyTo( matOut( rect ) );
}
if ( row < size.height - 1 )
{
cv::Rect rect1( 0, row + 1, size.width, size.height - row - 1 );
cv::Rect rect2( 0, row, size.width, size.height - row - 1 );
matIn( rect1 ).copyTo( matOut( rect2 ) );
}
matOut.copyTo(_matIn);
}
int main()
{
// Example case
Mat mat = (Mat_<uchar>(5, 5) << 1, 2, 3, 4, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 8, 0);
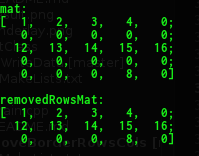
cout << "mat: " << endl << mat << endl;
// Find all non zero rows and set in a vector as indexes
Mat nonZeroCoordinates;
findNonZero(mat, nonZeroCoordinates);
vector<int> nonZeroRows;
for(size_t i = 0; i < nonZeroCoordinates.rows; ++i)
{
int row = nonZeroCoordinates.at<Point>(i).y;
if(!(std::find(nonZeroRows.begin(), nonZeroRows.end(), row) != nonZeroRows.end()))
{
//elem does not exists in the vector
nonZeroRows.push_back(row);
}
}
// Create a zeros rows indexer, according to the non zero indexes
vector<int> zeroRows(mat.cols);
std::iota(zeroRows.begin(), zeroRows.end(), 0);
std::sort(nonZeroRows.begin(), nonZeroRows.end());
for(int i = nonZeroRows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
zeroRows.erase( std::next( zeroRows.begin(), nonZeroRows[i] ) );
// remove rows
for(int i = 0; i < zeroRows.size(); ++i)
{
removeRow(mat, zeroRows[i]);
// decrease index values since the form of the mat changes
transform(zeroRows.begin(), zeroRows.end(), zeroRows.begin(), bind2nd(std::minus<int>(), 1));
}
cout << endl << "removedRowsMat: " << endl << mat << endl;
return 0;
}