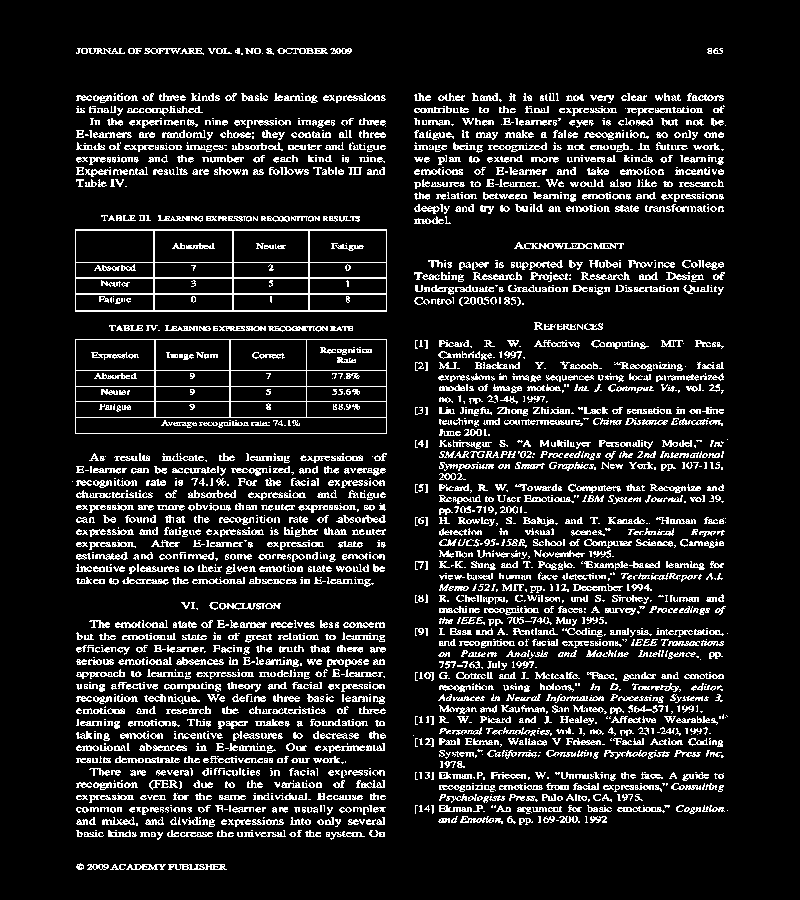
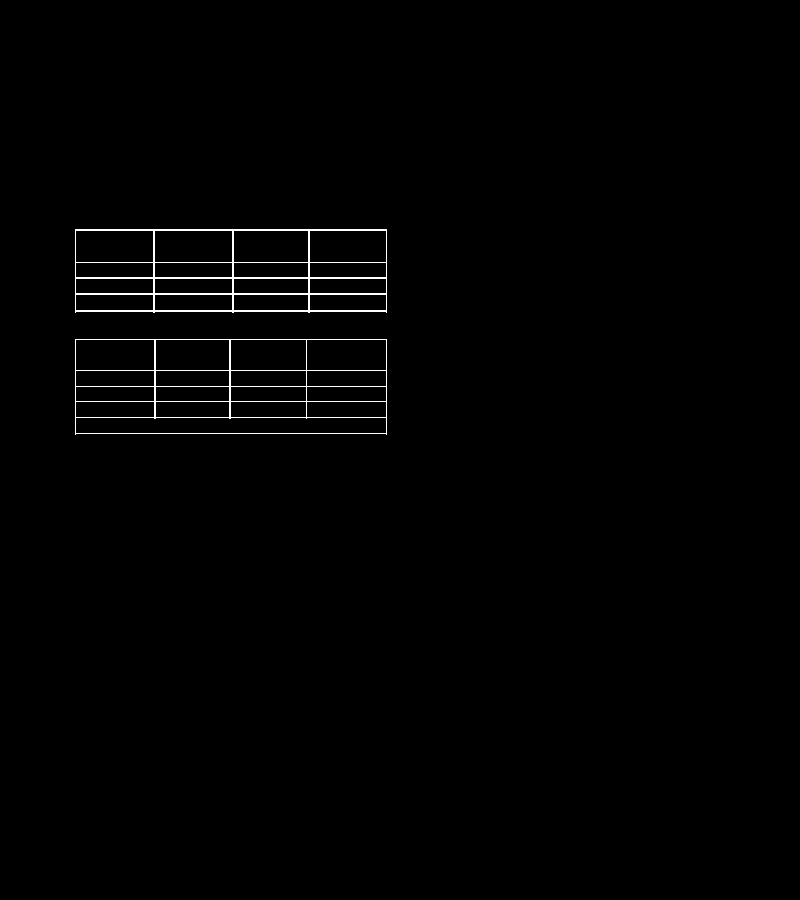
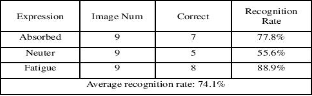
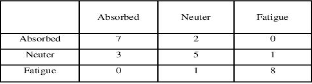
This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
As the others proposed finding the horizontal and vertical lines seems to be a nice way to go. Below you can find such a solution. In case you have any question feel free to ask, though I have added comments through my code so it should not be hard to follow.
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
// Load source image
string filename = "table.jpg";
Mat src = imread(filename);
// Check if image is loaded fine
if(!src.data)
cerr << "Problem loading image!!!" << endl;
// // Show source image
// imshow("src", src);
// resizing for practical reasons
Mat rsz;
Size size(800, 900);
resize(src, rsz, size);
imshow("rsz", rsz);
// Transform source image to gray if it is not
Mat gray;
if (rsz.channels() == 3)
{
cvtColor(rsz, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
}
else
{
gray = rsz;
}
// Show gray image
imshow("gray", gray);
// Apply adaptiveThreshold at the bitwise_not of gray, notice the ~ symbol
Mat bw;
adaptiveThreshold(~gray, bw, 255, CV_ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, THRESH_BINARY, 15, -2);
// Show binary image
imshow("binary", bw);
// Create the images that will use to extract the horizonta and vertical lines
Mat horizontal = bw.clone();
Mat vertical = bw.clone();
int scale = 15; // play with this variable in order to increase/decrease the amount of lines to be detected
// Specify size on horizontal axis
int horizontalsize = horizontal.cols / scale;
// Create structure element for extracting horizontal lines through morphology operations
Mat horizontalStructure = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(horizontalsize,1));
// Apply morphology operations
erode(horizontal, horizontal, horizontalStructure, Point(-1, -1));
dilate(horizontal, horizontal, horizontalStructure, Point(-1, -1));
// dilate(horizontal, horizontal, horizontalStructure, Point(-1, -1)); // expand horizontal lines
// Show extracted horizontal lines
imshow("horizontal", horizontal);

// Specify size on vertical axis
int verticalsize = vertical.rows / scale;
// Create structure element for extracting vertical lines through morphology operations
Mat verticalStructure = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size( 1,verticalsize));
// Apply morphology operations
erode(vertical, vertical, verticalStructure, Point(-1, -1));
dilate(vertical, vertical, verticalStructure, Point(-1, -1));
// dilate(vertical, vertical, verticalStructure, Point(-1, -1)); // expand vertical lines
// Show extracted vertical lines
imshow("vertical", vertical);

// create a mask which includes the tables
Mat mask = horizontal + vertical;
imshow("mask", mask);
// find the joints between the lines of the tables, we will use this information in order to descriminate tables from pictures (tables will contain more than 4 joints while a picture only 4 (i.e. at the corners))
Mat joints;
bitwise_and(horizontal, vertical, joints);
imshow("joints", joints);

// Find external contours from the mask, which most probably will belong to tables or to images
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point> > contours;
cv::findContours(mask, contours, hierarchy, CV_RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0));
vector<vector<Point> > contours_poly( contours.size() );
vector<Rect> boundRect( contours.size() );
vector<Mat> rois;
for (size_t i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
// find the area of each contour
double area = contourArea(contours[i]);
// // filter individual lines of blobs that might exist and they do not represent a table
if(area < 100) // value is randomly chosen, you will need to find that by yourself with trial and error procedure
continue;
approxPolyDP( Mat(contours[i]), contours_poly[i], 3, true );
boundRect[i] = boundingRect( Mat(contours_poly[i]) );
// find the number of joints that each table has
Mat roi = joints(boundRect[i]);
vector<vector<Point> > joints_contours;
findContours(roi, joints_contours, RETR_CCOMP, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
// if the number is not more than 5 then most likely it not a table
if(joints_contours.size() <= 4)
continue;
rois.push_back(rsz(boundRect[i]).clone());
// drawContours( rsz, contours, i, Scalar(0, 0, 255), CV_FILLED, 8, vector<Vec4i>(), 0, Point() );
rectangle( rsz, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1, 8, 0 );
}
for(size_t i = 0; i < rois.size(); ++i)
{
/* Now you can do whatever post process you want
* with the data within the rectangles/tables. */
imshow("roi", rois[i]);
waitKey();
}
imshow("contours", rsz);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
Of course you will need to try it by yourself and apply any modifications that might be needed depending on your dataset. Enjoy ;-).