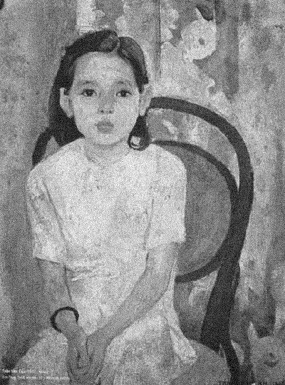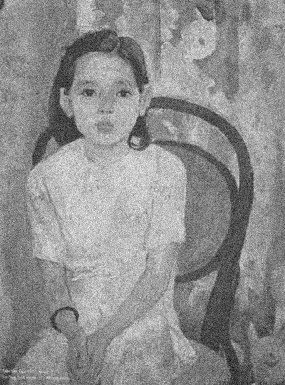This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
There may be two reasons for the results you got:
The code following works for me:
// imGray is the grayscale of the input image
cv::Mat noise = Mat(imGray.size(),CV_64F);
normalize(imGray, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::randn(noise, 0, 0.05);
result = result + noise;
normalize(result, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::imshow("OUTPUT",result);
And here is the illustration (an input image and Gaussian noise version with stddev=0.05 and 0.1, respectively):

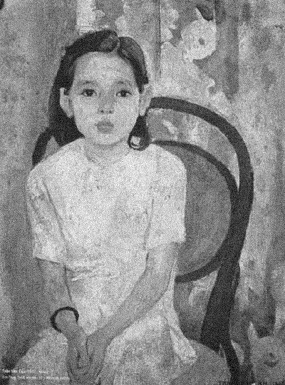
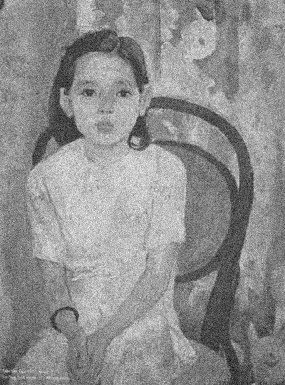
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
There may be two reasons for the results you got:
The code following works for me:
// imGray is the grayscale of the input image
cv::Mat noise = Mat(imGray.size(),CV_64F);
normalize(imGray, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::randn(noise, 0, 0.05);
result = result + noise;
normalize(result, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::imshow("OUTPUT",result);
And here is the illustration (an input image and Gaussian noise version with stddev=0.05 and 0.1, respectively):
respectively):

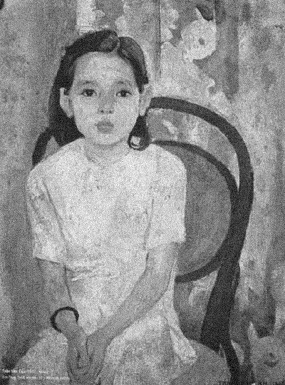
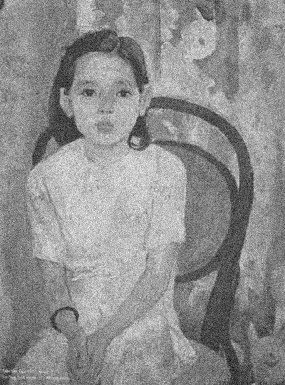
 | 3 | No.3 Revision |
There may be two reasons for the results you got:
The code following works for me:
// imGray is the grayscale of the input image
cv::Mat noise = Mat(imGray.size(),CV_64F);
normalize(imGray, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::randn(noise, 0, 0.05);
result = result + noise;
normalize(result, result, 0.0, 1.0, CV_MINMAX, CV_64F);
cv::imshow("OUTPUT",result);
And here is the illustration (an input image and Gaussian noise version versions with stddev=0.05 and 0.1, respectively):