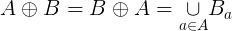This forum is disabled, please visit https://forum.opencv.org
 | 1 | initial version |
I would like to add some additional information even if mathematical morphology in general is out of my scope.
In image processing, the erosion operation can be defined for grayscale image and with a flat structuring element as:
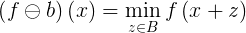
The destination image is set for each location to the minimum value of the pixels that lie in the structuring element chosen.
In a same way, the dilatation operation can be defined for grayscale image and with a flat structuring element as:
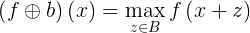
This time, the destination image is set for a particular position with the maximum value of the pixels of the source image that lie in the structuring element.
We have the same definition in the OpenCV documentation (e.g. cv::erode) or in the Matlab documentation (imerode).
This "general" definition can be applied for grayscale images and for binary images as well.
More specifically, the binary erosion of A by B is:
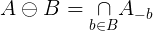
And the binary dilatation of A by B is: